Understanding the NCP1207ADR2G and Common Issues
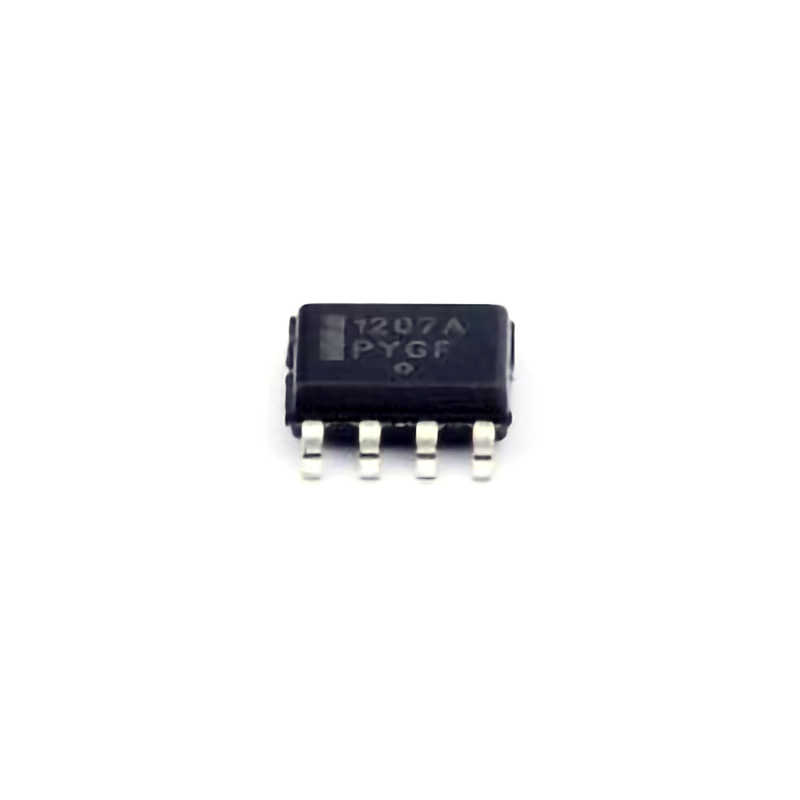
The NCP1207ADR2G is a highly reliable, cost-effective Power management IC that integrates a variety of features to enhance power efficiency in consumer electronics, industrial devices, and various other applications. This integrated circuit is primarily designed for use in power supplies, providing high-performance switching regulators with low standby power consumption. However, like all electronic components, the NCP1207ADR2G can face occasional issues that may affect its performance. Understanding the common problems and their solutions can help ensure that the IC continues to function optimally.
1. Power Supply Failure
One of the most common issues faced by users of the NCP1207ADR2G is power supply failure. This can manifest as an inability to turn on or a sudden shutdown of the device. There are several potential causes for power supply failure, including incorrect component placement, insufficient input voltage, or issues within the IC itself.
Solution:
Check Input Voltage: Ensure that the input voltage to the NCP1207ADR2G is within the specified range (typically 6V to 24V). Insufficient input voltage can prevent the IC from functioning properly.
Examine External Components: Verify that all external components (such as resistors, capacitor s, and diodes) connected to the IC are correctly placed according to the datasheet. Improper placement or faulty components can cause power failures.
Test the IC: If the above steps do not resolve the issue, it may be necessary to test the NCP1207ADR2G itself. Use a multimeter to check the output voltage and ensure that it is within the specified range. If not, consider replacing the IC.
2. Overheating and Thermal Shutdown
Overheating is another common issue with the NCP1207ADR2G. The IC may shut down or enter a thermal protection mode if it becomes too hot. This can happen if the power dissipation exceeds the thermal limits, often due to excessive current or inadequate heat dissipation.
Solution:
Improve Heat Dissipation: Ensure proper heat sinking and airflow around the IC. Consider adding a heatsink or improving the PCB design to help dissipate heat more effectively.
Check for Short Circuits: Short circuits in the circuit can cause excessive current draw, leading to overheating. Use a thermal camera or temperature sensor to detect hot spots and identify any short circuits or other issues.
Reduce Input Voltage: Lowering the input voltage may reduce the overall power dissipation and help manage heat more effectively.
3. Inconsistent Output Voltage
Inconsistent output voltage can be a major problem when using the NCP1207ADR2G in power supply circuits. Fluctuations or noise in the output voltage can lead to instability in the entire system, affecting the performance of other components.
Solution:
Check Feedback Loop: The NCP1207ADR2G uses a feedback loop to regulate output voltage. If there is a problem with the feedback network, the output voltage may fluctuate. Verify that the feedback resistor values are correct and that there is no damage to the feedback loop components.
Ensure Proper Capacitor Selection: The output voltage stability can also be affected by the choice of Capacitors . Ensure that the output capacitors meet the required specifications and are of high quality. Use low ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance ) capacitors to improve voltage stability.
Reduce Noise: Electromagnetic interference ( EMI ) can introduce noise in the power supply, causing fluctuations in the output voltage. Shielding the circuit or using proper grounding techniques can help reduce EMI and improve voltage consistency.
4. Output Ripple and Noise
Output ripple and noise are a common issue in switching regulators like the NCP1207ADR2G. These fluctuations can cause instability in sensitive electronics, especially in applications like audio equipment or communication devices.
Solution:
Use Low ESR Capacitors: Low ESR capacitors are highly effective in filtering out high-frequency noise and ripple. Ensure that you are using high-quality electrolytic or ceramic capacitors at the output.
Place Capacitors Close to the IC: For maximum effectiveness, place the output capacitors as close as possible to the IC. This minimizes the impedance and helps to filter out ripple more effectively.
Increase Filtering Stages: Adding additional stages of filtering (e.g., more capacitors or inductors) can further reduce ripple and noise. A common configuration involves adding a second-stage low-pass filter to improve output quality.
5. Switching Frequency Issues
The NCP1207ADR2G operates at a fixed switching frequency that is designed to balance efficiency and power performance. However, if the switching frequency becomes erratic or mismatched, it can lead to poor performance, excessive heat, or malfunctioning.
Solution:
Check Timing Components: The switching frequency of the NCP1207ADR2G is determined by the external timing resistor and capacitor. Make sure these components are of the correct value and are functioning properly.
Examine for Oscillations: If the switching frequency is unstable, the circuit may be oscillating. Check for unwanted oscillations and ensure that the timing components are not defective.
Verify Grounding: Improper grounding can lead to instability in the switching frequency. Ensure that the IC’s ground pin is properly connected to a solid ground plane, minimizing the risk of erratic frequency behavior.
Advanced Troubleshooting Solutions and Preventive Measures
6. Incorrect Startup Behavior
When the NCP1207ADR2G is powered on, it should start up smoothly and without delay. However, sometimes the IC might fail to start properly, showing a delay or erratic startup behavior. This can be caused by incorrect component selection, inadequate startup circuitry, or issues with the soft-start functionality.
Solution:
Check Soft-Start Capacitor: The NCP1207ADR2G includes a soft-start feature to limit inrush current. Ensure that the soft-start capacitor is correctly sized and placed. A damaged or incorrect capacitor can cause startup issues.
Verify Startup Circuitry: Review the startup circuitry to make sure there are no issues with the input voltage or external components that might delay or prevent proper startup.
Monitor Voltage Waveforms: Use an oscilloscope to monitor the voltage waveforms during startup. This can help you identify any issues with the power-up sequence.
7. Overcurrent Protection Activation
The NCP1207ADR2G is designed with built-in overcurrent protection to prevent damage in case of excessive current draw. However, in some cases, the overcurrent protection may be triggered unnecessarily, leading to system shutdown or underperformance.
Solution:
Reduce Load Current: Check the load current to ensure it is within the IC’s maximum rated output. If the load is too high, consider reducing it or using a higher-rated power supply IC.
Examine the External Circuit: The external circuit components, such as inductors and diodes, could also be contributing to excessive current draw. Verify that these components are correctly rated for the application.
Enable Soft-Start Feature: The NCP1207ADR2G features a soft-start function that gradually ramps up the output current. Enabling this feature can help avoid triggering overcurrent protection during startup.
8. Capacitor Quality and Placement
Capacitors play a crucial role in stabilizing the output and filtering noise. Low-quality or improperly placed capacitors can cause significant issues, including instability, noise, and poor power performance.
Solution:
Choose High-Quality Capacitors: Always choose high-quality capacitors with low ESR and high voltage ratings. This ensures stable performance and reduces the risk of capacitor failure.
Place Capacitors Correctly: Ensure that the input and output capacitors are placed as close to the IC as possible. This minimizes the impedance and maximizes the filtering effect.
9. PCB Layout Considerations
A poor PCB layout can exacerbate many of the problems listed above, including overheating, power loss, and instability. Proper layout is essential for the reliable operation of the NCP1207ADR2G.
Solution:
Minimize Ground Bounce: Use a solid ground plane to minimize ground bounce and noise. Keep the current-carrying paths as short and wide as possible to reduce resistance and inductance.
Use Separate Traces for Power and Signal: Separate power and signal traces to prevent noise from interfering with sensitive signal paths. Keep high-current paths away from the IC’s control and feedback pins.
Ensure Adequate Via Size: Make sure that vias used in the PCB design are large enough to handle the current without causing excessive resistance.
Conclusion
The NCP1207ADR2G is a versatile and efficient power management IC that can be used in a variety of electronic applications. By understanding the common issues it may face and applying the appropriate troubleshooting steps, users can ensure reliable and stable performance from the IC. Whether it’s dealing with power supply failure, output ripple, overheating, or other issues, following the solutions provided can help maintain the NCP1207ADR2G’s optimal operation in your designs.
By taking the time to carefully select components, optimize PCB layout, and test each step of the circuit, users can avoid many of the common pitfalls that can arise with power management ICs, ultimately leading to a more robust and efficient electronic system.
If you are looking for more information on commonly used Electronic Components Models or about Electronic Components Product Catalog datasheets, compile all purchasing and CAD information into one place.
Partnering with an electronic components supplier sets your team up for success, ensuring the design, production, and procurement processes are quality and error-free.